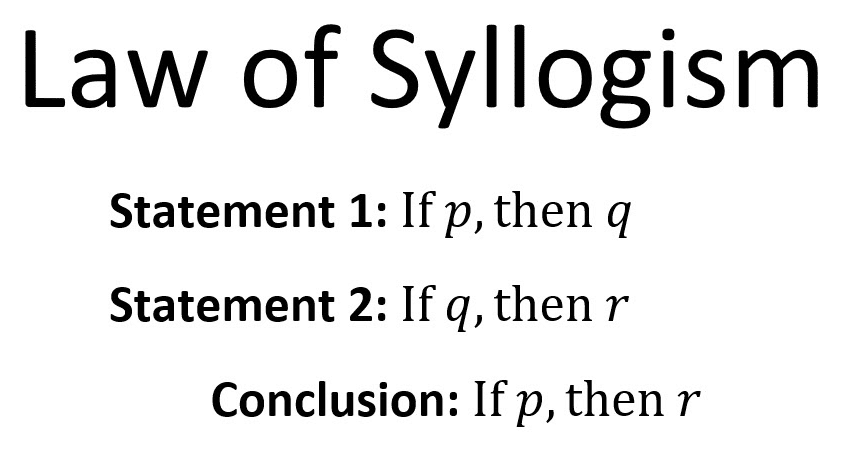Understanding the Law of Syllogism: A Comprehensive Guide
The Law of Syllogism is a fundamental concept in the field of logic and reasoning. It serves as a powerful tool for drawing conclusions based on two conditional statements. In this extensive article, we will delve deep into the Law of Syllogism, explore its various aspects, provide practical examples, and address common questions related to this essential logical principle.
Introduction to the Law of Syllogism
The Law of Syllogism, often referred to as the Law of Hypothetical Syllogism, is a logical rule that enables us to infer a conclusion from two conditional statements. This law forms the basis for valid deductive reasoning, a fundamental component of both formal and informal logic.
Basic Elements of the Law of Syllogism
Before we delve into the intricacies of the Law of Syllogism, it is essential to understand the basic components involved:
- Conditional Statements: These are statements that express a conditional relationship, typically in the form of “if…then…” propositions.
- Premises: In the context of the Law of Syllogism, these are the two conditional statements that serve as the starting point for drawing a conclusion.
- Conclusion: The outcome of applying the Law of Syllogism, which derives a new conditional statement based on the premises.
Formulation of the Law of Syllogism
The Law of Syllogism can be expressed as follows:
If “If P, then Q” is true, and “If Q, then R” is true, then “If P, then R” is also true.
In other words, if we have two conditional statements, and the consequent (Q) of the first statement matches the antecedent (Q) of the second statement, we can infer a new conditional statement where the antecedent (P) of the first statement implies the consequent (R) of the second statement.
Example of the Law of Syllogism
Let’s illustrate the Law of Syllogism with a practical example:
- If it rains, the ground gets wet. (If P, then Q)
- If the ground gets wet, plants grow. (If Q, then R)
By applying the Law of Syllogism, we can deduce:
- If it rains, plants grow. (If P, then R)
In this case, the Law of Syllogism has allowed us to draw a logical conclusion from the two conditional statements.
Common Misconceptions
There are several misconceptions and points of confusion regarding the Law of Syllogism:
1. Equivalence vs. Implication
The Law of Syllogism deals with logical implication, not equivalence. It is not concerned with whether P and R are equivalent but rather whether R can be inferred from P based on the given conditional statements.
2. Strict Application
The Law of Syllogism is not a standalone tool for all logical reasoning. It applies specifically to situations involving two conditional statements.
Practical Applications
The Law of Syllogism has real-world applications in various fields, including:
- Mathematics: In proving theorems and making mathematical deductions.
- Philosophy: In constructing valid arguments and evaluating the soundness of reasoning.
- Computer Science: In programming and algorithm design.
- Science: In forming hypotheses and drawing logical conclusions from experimental data.
Limitations and Constraints
While the Law of Syllogism is a powerful tool, it has its limitations:
- It only applies to situations with two conditional statements. More complex scenarios may require additional logical rules.
- The accuracy of the conclusion depends on the validity of the premises. If the premises are false, the conclusion may also be false.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the Law of Syllogism, and why is it important?
The Law of Syllogism is a fundamental principle of deductive reasoning that allows us to draw conclusions from two conditional statements. It is important because it forms the basis for logical deduction in various fields, including mathematics, philosophy, and computer science.
2. Can you provide an example of a syllogism?
Certainly! A classic example of a syllogism is:
- All humans are mortal. (Major premise)
- Socrates is a human. (Minor premise)
- Therefore, Socrates is mortal. (Conclusion)
3. How does the Law of Syllogism differ from the Law of Modus Ponens?
The Law of Syllogism deals with drawing conclusions from two conditional statements, while the Law of Modus Ponens focuses on drawing conclusions from a single conditional statement. In Modus Ponens, if “If P, then Q” is true, and P is true, then Q can be inferred.
4. What are the limitations of the Law of Syllogism?
The primary limitations of the Law of Syllogism are that it applies specifically to two conditional statements and that the validity of the conclusion depends on the accuracy of the premises. If the premises are false, the conclusion may also be false.
5. Can the Law of Syllogism be used in everyday decision-making?
While the Law of Syllogism is a fundamental logical principle, it is not typically used in everyday decision-making. It is more commonly applied in academic, scientific, and philosophical contexts to ensure rigorous and valid reasoning.
6. Are there any other laws of logic related to syllogisms?
Yes, there are other laws of logic, such as the Law of Modus Tollens, Law of Contrapositive, and Law of Transitivity, which are related to syllogistic reasoning and are used to draw valid conclusions based on specific logical structures.
7. Can the Law of Syllogism be applied in legal arguments?
Yes, the Law of Syllogism can be applied in legal arguments to draw conclusions from two conditional statements. Lawyers and judges often use logical reasoning to construct and evaluate legal arguments.
8. How can I improve my skills in using the Law of Syllogism?
Improving your skills in using the Law of Syllogism involves practicing with various examples and honing your ability to identify valid conclusions based on given premises. Additionally, studying formal logic and taking courses in logic can be helpful.
9. Are there cultural or linguistic variations in the application of the Law of Syllogism?
The Law of Syllogism is a fundamental principle of deductive reasoning and is not influenced by cultural or linguistic variations. It is a universal concept in the field of logic.
10. Can the Law of Syllogism be used in scientific research?
Yes, the Law of Syllogism can be applied in scientific research, especially when scientists are drawing conclusions based on conditional statements and logical reasoning. It helps ensure that scientific hypotheses and conclusions are logically sound.
Conclusion
The Law of Syllogism is a vital tool for logical reasoning, allowing us to draw conclusions from two conditional statements. Understanding its principles and applications can enhance our ability to think critically and make valid deductions in various fields, from mathematics and philosophy to science and law. By exploring the common questions and misconceptions surrounding this law, we have deepened our understanding of its significance in the world of logic and reasoning.